UVXY, VXX Volatility ETPs: How Do Long Volatility ETPs Work?
Volatility Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs) have become increasingly popular among traders and investors seeking to capitalize on market volatility. In this blog post, we’ll explore long volatility Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs), with a focus on UVXY and VXX. We’ll examine their origins, inner workings, and practical applications in trading strategies. Additionally, we’ll discuss the potential advantages and important considerations for traders and investors interested in these sophisticated financial instruments.
A Brief History of UVXY and VXX
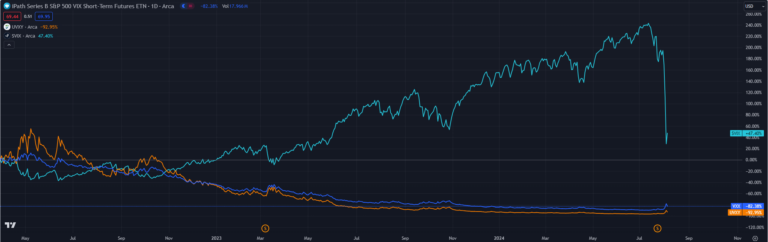
UVXY (ProShares Ultra VIX Short-Term Futures ETF) and VXX (iPath Series B S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures ETN) are two well-known long volatility ETPs that have played significant roles in the volatility trading landscape. These products were introduced to provide investors with exposure to market volatility without directly trading VIX futures contracts.
VXX was first launched in 2009, offering investors a way to gain exposure to short-term VIX futures. UVXY, introduced in 2011, aimed to provide leveraged exposure to the same market, typically seeking to deliver 1.5x the daily performance of its underlying index.
How Long Volatility ETPs Work
To understand how UVXY and VXX function, it’s crucial to first grasp the concept of the VIX and its futures.
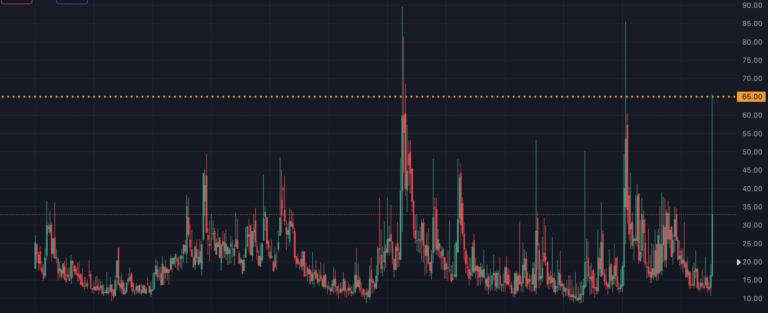
The VIX, or CBOE Volatility Index, is often referred to as the “fear index.” It measures the market’s expectation of 30-day volatility implied by S&P 500 index options. A higher VIX value indicates greater expected volatility, while a lower value suggests calmer market conditions.
VIX futures are contracts based on the expected value of the VIX at a future date. These futures contracts are the primary instruments used by long volatility ETPs to gain exposure to market volatility.
UVXY and VXX work by maintaining a rolling portfolio of first- and second-month VIX futures contracts. As these contracts approach expiration, the ETPs “roll” their positions by selling near-term contracts and purchasing longer-dated ones. This process aims to maintain consistent exposure to short-term volatility expectations.
It’s important to note that these ETPs don’t directly track the VIX index. Instead, they follow indexes that represent a mix of short-term VIX futures. This distinction can lead to significant differences between the performance of the ETPs and the VIX itself, especially over extended periods.
Scenarios and Examples of Trader Usage
Traders employ long volatility ETPs like UVXY and VXX in various scenarios:
- Hedging: Investors might use these products to protect their portfolios against potential market downturns. Since volatility tends to spike during market sell-offs, long volatility ETPs can provide a hedge against losses in other positions.
- Speculation: Some traders use these ETPs to bet on increased market volatility. For example, if a trader anticipates a major economic announcement that could cause market turbulence, they might buy UVXY or VXX in anticipation of a volatility spike.
- Mean reversion trades: Experienced traders might use these products as part of more complex strategies, such as volatility mean reversion trades. This involves shorting volatility when it’s high and covering (buying back) when it’s lower, based on the assumption that volatility tends to revert to its long-term average.
- Short-term trading: Due to their sensitivity to market movements, these ETPs are often used for short-term trading strategies, allowing traders to capitalize on quick market swings.
Benefits and Risks
Benefits of trading long volatility ETPs include:
- Exposure to volatility without directly trading VIX futures
- Potential for significant gains during market turmoil
- Useful tools for portfolio hedging
- Liquidity and ease of trading compared to direct futures trading
However, traders should be aware of several risks:
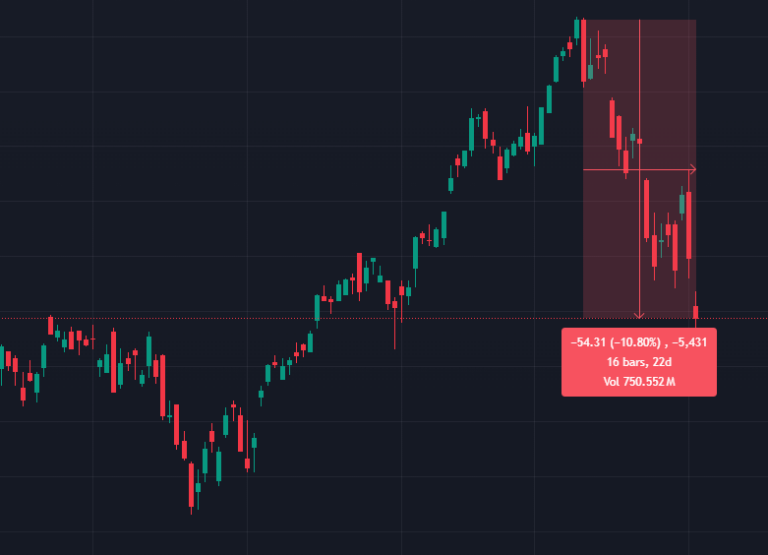
- Decay over time: Due to the constant rolling of futures contracts and the typically upward-sloping VIX futures curve (the difference between each different months futures contract price), these ETPs tend to lose value over time in neutral or bullish markets.
- Leverage risks: Leveraged products like UVXY can amplify losses as well as gains.
- Complexity: The relationship between these ETPs, VIX futures, and the VIX index itself can be complex and counterintuitive.
- Volatility of volatility: These products can be extremely volatile themselves, leading to rapid and significant price swings.
- Potential for significant losses: In prolonged periods of low volatility, these ETPs can experience substantial declines.
Understanding long volatility ETPs like UVXY and VXX requires a grasp of complex market dynamics. While these products can offer unique opportunities for traders and investors, they also come with significant risks. As with any sophisticated financial instrument, thorough research and a clear understanding of the underlying mechanisms are essential before incorporating these ETPs into a trading or investment strategy.